OpenGL ES on iOS — Assimp
简述
本文主要记录 Assimp库的编译和使用,可能会有不准确的地方,还望多多指正共同学习~
Assimp是Open Asset Import Library(开放的资产导入库)的缩写。Assimp能够导入很多种不同的模型文件格式(并也能够导出部分的格式),它会将所有的模型数据加载至Assimp的通用数据结构中
Assimp编译
这里是库的github地址Assimp,下载下来 我们还要编译成iOS可用的库(这里踩坑不少/(ㄒoㄒ)/~~)
配置CMAKE环境
CMake是个开源的跨平台自动化建构系统,想要编译Assimp 先要配置好它~ CMake官网
然后将Cmake链接至终端
1
| sudo "/Applications/CMake.app/Contents/bin/cmake-gui" --install
|
编译 Assimp.a
切换至目标路径
执行下面命令~
1
2
| //将你需要支持的架构输入 一般就是X86 和 arm64
./build.sh --stdlib=libc++ --archs="arm64 x86_64"
|
这是你的 lib文件夹下就是这个样子的~
但是这样子 还是不能在iOS上用的哦~ 因为 XML.a只支持 X86架构~ 我们还需要额外编译它
XML.a
这时就要使用CMake客户端了~ 创建一个空的build文件夹~,使用Xcode 默认配置生成~
这时就根据需要编译出自己需要的静态库即可了~~
Assimp使用
模型结构
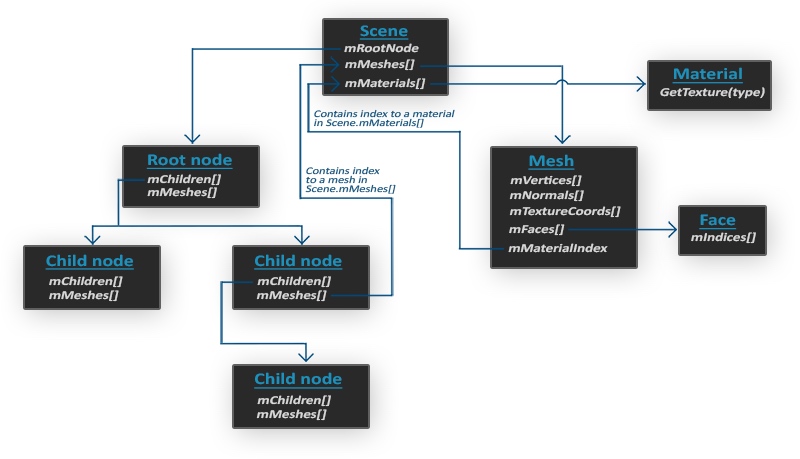
当Assimp加载模型时,会将模型数据加载到Scene(场景)对象中.
Scene中会有一个Mesh(网格)对象,在Mesh中包含着渲染所需的所有数据,如顶点,法向量,纹理坐标…
在Mesh中包含一个Material对象,其中是关于材质的数据(镜面贴图,漫反射贴图,法向量贴图….)
在Mesh中还包含了许多Face,Face其实是指物体的渲染图元,一个面包含了组成图元的顶点索引(这里其实就相当于之前讲到的EBO)
Scene中会包含一个根节点,在根节点之下会有很多子节点~节点中有指向Mesh中数据的索引
所以我们需要做的就是将Scene中的节点遍历,然后将节点中的数据提取出来,以适合的格式输入到着色器中~~(๑•ᴗ•๑)
代码
定义 Mesh类 和 Model类
Mesh类对应每个节点的网格数据,Model则对应Scene对象~
我展示的代码主要是和Assimp相关的内容~
头文件
1
2
3
| #include "assimp/Importer.hpp"
#include "assimp/scene.h"
#include "assimp/postprocess.h"
|
属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| //顶点
struct Vertex {
glm::vec3 Position;
glm::vec3 Normal;
glm::vec2 TexCoords;
};
struct Vertex {
glm::vec3 Position;
glm::vec3 Normal;
glm::vec2 TexCoords;
};
class Mesh {
std::vector<Vertex> vertices; //顶点
std::vector<unsigned int> indices; //索引
std::vector<Texture> textures; //纹理
unsigned int VAO, VBO, EBO;
}
class Model{
std::vector<Texture> textures_loaded; //缓冲纹理,避免多次加载
std::vector<Mesh> meshes; //节点数据数组
std::string directory; //加载路径
}
|
加载Scene
遍历根节点及其下属所有子节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| Assimp::Importer import;
//获取Scene
const aiScene *scene = import.ReadFile(path, aiProcess_Triangulate | aiProcess_FlipUVs);
if(!scene || scene->mFlags & AI_SCENE_FLAGS_INCOMPLETE || !scene->mRootNode)
{
printf("ERROR::ASSIMP:: %s",import.GetErrorString());
return;
}
directory = path.substr(0, path.find_last_of('/'));
processNode(scene->mRootNode, scene);
|
ReadFile将指定路径的模型加载,Path为路径,后面的是加载时的额外处理
aiProcess_Triangulate将加载的图元变换为三角形
aiProcess_FlipUVs翻转纹理坐标Y轴(OpenGL的纹理Y轴是翻的~)
aiProcess_GenNormals 若模型不包含法向量的话,就为每个顶点创建法线
aiProcess_SplitLargeMeshes将较大的网格分割为较小的网格(当渲染有最大顶点数量要求时)
aiProcess_OptimizeMeshes将较小的网格们拼接为较大的一个网格(减少绘制调用)
指令大全~~
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| void processNode(aiNode *node, const aiScene *scene){
//提取节点数据~
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < node->mNumMeshes; i++)
{
aiMesh *mesh = scene->mMeshes[node->mMeshes[i]];
meshes.push_back(processMesh(mesh, scene));
}
//递归遍历
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < node->mNumChildren; i++)
{
processNode(node->mChildren[i], scene);
}
}
|
提取节点网格数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
| Mesh processMesh(aiMesh *mesh, const aiScene *scene) {
//需要提取的数据~
std::vector<Vertex> vertices;
std::vector<unsigned int> indices;
std::vector<Texture> textures;
//将顶点数据提取
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < mesh->mNumVertices; i++)
{
Vertex vertex;
glm::vec3 vector;
// positions
vector.x = mesh->mVertices[i].x;
vector.y = mesh->mVertices[i].y;
vector.z = mesh->mVertices[i].z;
vertex.Position = vector;
// normals
vector.x = mesh->mNormals[i].x;
vector.y = mesh->mNormals[i].y;
vector.z = mesh->mNormals[i].z;
vertex.Normal = vector;
if(mesh->mTextureCoords[0]) {
glm::vec2 vec;
vec.x = mesh->mTextureCoords[0][i].x;
vec.y = mesh->mTextureCoords[0][i].y;
vertex.TexCoords = vec;
}
else
vertex.TexCoords = glm::vec2(0.0f, 0.0f);
vertices.push_back(vertex);
}
//将索引数据提取
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < mesh->mNumFaces; i++)
{
aiFace face = mesh->mFaces[i];
for(unsigned int j = 0; j < face.mNumIndices; j++)
indices.push_back(face.mIndices[j]);
}
//将纹理数据提取(漫反射纹理,镜面纹理...)
aiMaterial* material = scene->mMaterials[mesh->mMaterialIndex];
std::vector<Texture> diffuseMaps = loadMaterialTextures(material, aiTextureType_DIFFUSE, "texture_diffuse");
textures.insert(textures.end(), diffuseMaps.begin(), diffuseMaps.end());
std::vector<Texture> specularMaps = loadMaterialTextures(material, aiTextureType_SPECULAR, "texture_specular");
textures.insert(textures.end(), specularMaps.begin(), specularMaps.end());
std::vector<Texture> normalMaps = loadMaterialTextures(material, aiTextureType_HEIGHT, "texture_normal");
textures.insert(textures.end(), normalMaps.begin(), normalMaps.end());
std::vector<Texture> heightMaps = loadMaterialTextures(material, aiTextureType_AMBIENT, "texture_height");
textures.insert(textures.end(), heightMaps.begin(), heightMaps.end());
return Mesh(vertices, indices, textures);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
| std::vector<Texture> loadMaterialTextures(aiMaterial *mat, aiTextureType type,std::string typeName) {
std::vector<Texture> textures;
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < mat->GetTextureCount(type); i++)
{
aiString str;
mat->GetTexture(type, i, &str);
//检查纹理是否之前已经加载过,
bool skip = false;
for(unsigned int j = 0; j < textures_loaded.size(); j++)
{
if(std::strcmp(textures_loaded[j].path.data(), str.C_Str()) == 0)
{
textures.push_back(textures_loaded[j]);
skip = true; // a texture with the same filepath has already been loaded, continue to next one. (optimization)
break;
}
}
if(!skip)
{ // if texture hasn't been loaded already, load it
//若纹理未加载,则加载
Texture texture;
texture.id = TextureFromFile(str.C_Str(), this->directory);
texture.type = typeName;
texture.path = str.C_Str();
textures.push_back(texture);
textures_loaded.push_back(texture);
}
}
return textures;
}
//将纹理加载,输入到着色器
unsigned int TextureFromFile(const char *path, const std::string &directory, bool gamma)
{
std::string filename = std::string(path);
filename = directory + '/' + filename;
unsigned int textureID;
glGenTextures(1, &textureID);
int width, height, nrComponents;
unsigned char *data = stbi_load(filename.c_str(), &width, &height, &nrComponents, 0);
if (data)
{
GLenum format;
if (nrComponents == 1)
format = GL_RED;
else if (nrComponents == 3)
format = GL_RGB;
else if (nrComponents == 4){
for (int i = 0; i<width*height; i++ ) {
char tR = data[i*4+2];
data[i*4+2] = data[i*4];
data[i*4] = tR;
}
format = GL_RGBA;
}
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureID);
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, format, width, height, 0, format, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR_MIPMAP_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
stbi_image_free(data);
}
else
{
//std::cout << "Texture failed to load at path: " << path << std::endl;
printf("Texture failed to load at path: %s",path);
stbi_image_free(data);
}
return textureID;
}
|
注意
在加载模型数据时,需要注意的是 模型并不一定会提供完整的贴图,例如 有的简单模型,建模师有可能不会为其添加贴图,而是给模型设置一种高光材质,以节约资源.这时 材质信息存储在mtl文件中,而且还有可能连mtl文件也没有, 这时 则需要我们添加默认材质~
.mtl文件(Material Library File)是材质库文件,描述的是物体的材质信息,ASCII存储,任何文本编辑器可以将其打开和编辑。一个.mtl文件可以包含一个或多个材质定义,对于每个材质都有其颜色,纹理和反射贴图的描述,应用于物体的表面和顶点。想详细了解的朋友们可以看这里.obj文件格式与.mtl文件格式
绘制
绘制就很简单了,将提取出来的每个网格的数据 传入着色器就好~
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| void Draw(GLuint program){
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
unsigned int diffuseNr = 1;
unsigned int specularNr = 1;
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < textures.size(); i++)
{
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0 + i);
std::stringstream ss;
std::string number;
std::string name = textures[i].type;
if(name == "texture_diffuse")
ss << diffuseNr++;
else if(name == "texture_specular")
ss << specularNr++;
number = ss.str();
glUniform1i(glGetUniformLocation(program, ("material." + name + number).c_str()), i);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textures[i].id);
}
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, indices.size(), GL_UNSIGNED_INT, 0);
}
|
在着色器中,也就是将获取的顶点数据 和 纹理 按照需要进行输出就好了~ 和 绘制木箱子无异~

结尾
我对这一块的内容也并不是十分熟练,所以Assimp使用这里有些粗略,以后有啥新的收获也会补上~ 倒是Assimp库编译那里 我是踩了好多坑~






